- Application description
- Raman spectroscopy
- FT-IR spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy provides sample information at the molecular level, which can be used to advantage in the analysis of various types of polyethylene. This method requires almost no sample treatment, is fast, non-destructive and, with the help of the TQ Analyst program, it is possible to perform quantitative measurements for almost every application.
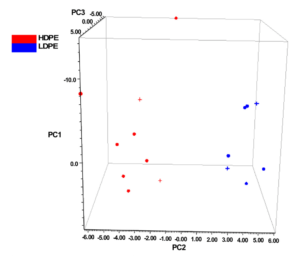
Polyethylene (PE) is currently one of the most produced plastics in the world. According to density, they are divided into low-density (LDPE) and high-density (HDPE) polyethylene, which have fundamentally different physical, chemical and mechanical properties, and therefore also the way they are used. While HDPE is mainly used for the production of various containers and tubes, LDPE is the starting material for the production of bags and similar packaging.
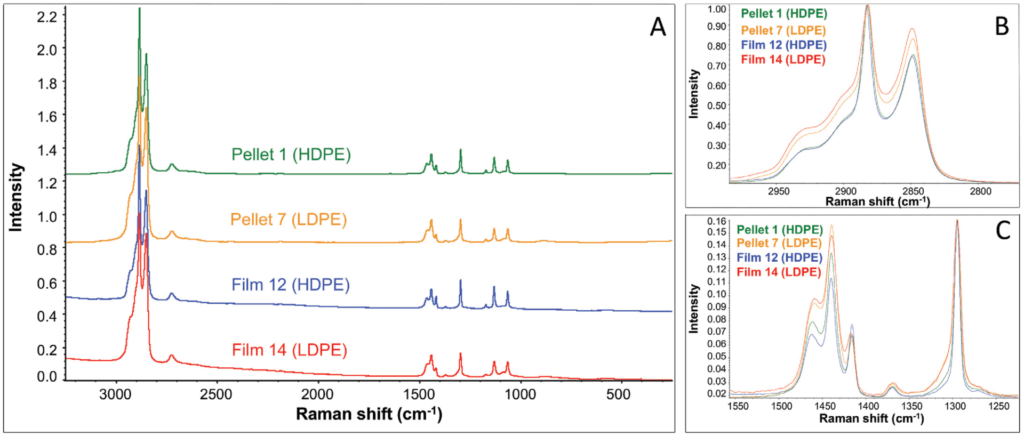
Both types of polyethylene are produced in the form of pellets, which are then further processed into films or tubes. Their density is conventionally measured by density gradient or ultrasound, but these techniques require PE in its pure form, which can be e.g. in the case of films a problem. Therefore, it is appropriate to combine traditional methods with Raman spectroscopy – with a Nicolet DXR3 or DXR3xi microscope.
With the help of it it is possible not only to determine the chemical composition of the analyzed substance, but also to determine its concentration, or conformational changes, changes in bonds and other parameters that can facilitate and streamline production. In addition, with TQ Analystyou can create methods that can be used to easily and quickly distinguish between different types of PE.